Muscle Loss in Men: How to Reverse Age-Related Decline
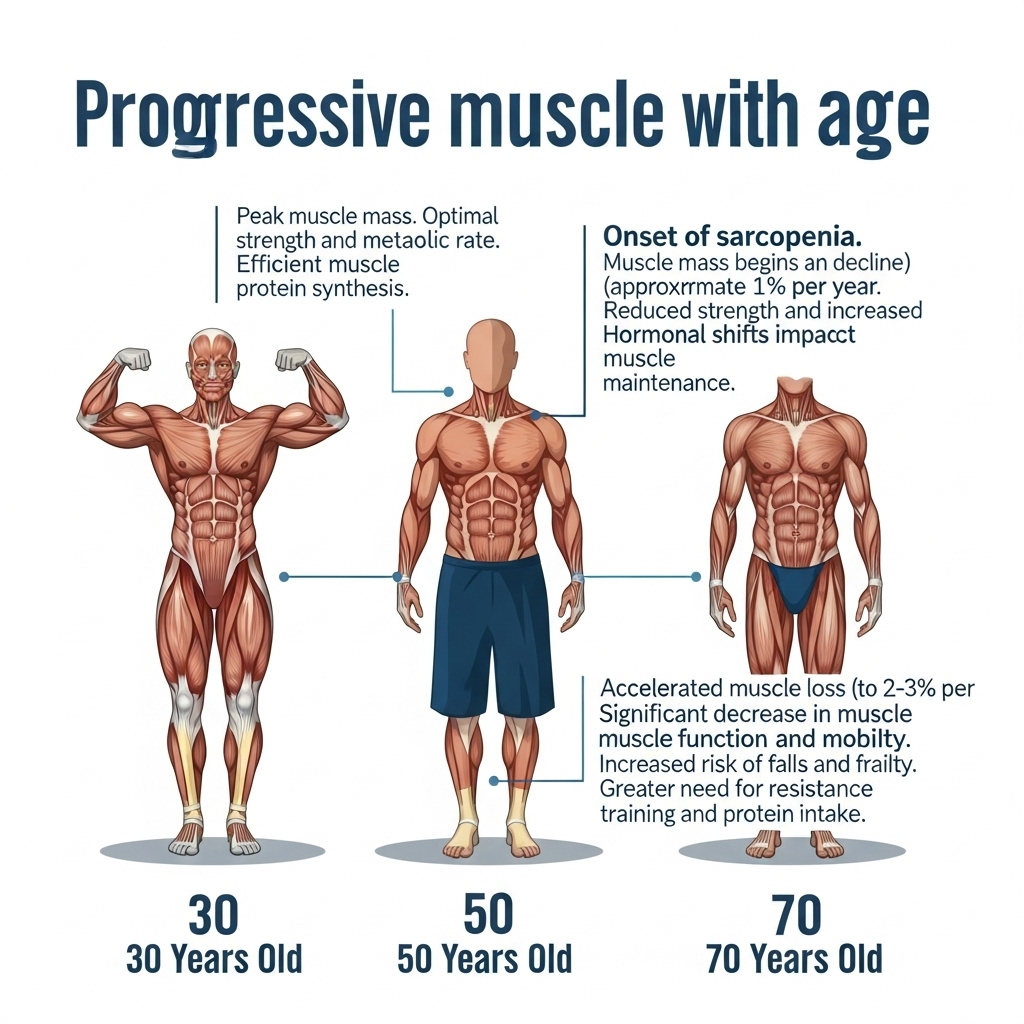
As men age, they often notice changes in their body that go beyond gray hair and wrinkles. One of the most significant — yet often overlooked — changes is muscle loss, medically known as sarcopenia. This gradual decline in muscle mass and strength can start as early as your 30s and accelerate after the age of 50. While some degree of muscle loss is a natural part of aging, the good news is that it’s not irreversible.
In this guide, we’ll explore why muscle loss happens, its effects on health, and how to reverse and prevent it through proven strategies in exercise, diet, and lifestyle.

Understanding Age-Related Muscle Loss
Muscle loss isn’t just about looking less muscular — it affects overall health, mobility, metabolism, and even your independence as you get older.
What is Sarcopenia?
Sarcopenia is the age-related loss of skeletal muscle mass and strength. On average, men lose 3–5% of muscle mass per decade after age 30. By the time they reach 70, some may have lost more than 25–30% of their original muscle mass.
Why Does Muscle Loss Happen?
Several factors contribute to age-related muscle decline:
- Hormonal Changes – Testosterone, growth hormone, and insulin-like growth factor (IGF-1) naturally decline with age, reducing muscle protein synthesis.
- Reduced Physical Activity – Sedentary lifestyles accelerate muscle atrophy.
- Poor Nutrition – Inadequate protein intake slows muscle repair and growth.
- Chronic Inflammation – Low-grade inflammation damages muscle tissue over time.
- Nerve and Muscle Changes – Motor neurons deteriorate, affecting muscle fibers.
Why Muscle Loss Matters for Men’s Health
Losing muscle is more than a cosmetic concern — it impacts nearly every aspect of health.
- Slower Metabolism – Muscle burns more calories at rest than fat, so losing muscle can lead to weight gain.
- Reduced Strength & Endurance – Everyday tasks like climbing stairs or carrying groceries become harder.
- Poor Balance & Mobility – Muscle loss increases the risk of falls and injuries.
- Weaker Immune Function – Muscle plays a role in immune response and recovery.
- Lower Quality of Life – Less muscle means less independence and more limitations.
Signs You’re Losing Muscle
You may be experiencing muscle loss if you notice:
- Decreased strength (struggling to lift weights you used to handle easily)
- Shrinking arms, legs, or chest muscles
- Fatigue after light activity
- More body fat despite no changes in diet
- Difficulty with balance and coordination
How to Reverse Age-Related Muscle Loss
The most effective way to combat muscle loss is a three-pronged approach: strength training, proper nutrition, and lifestyle adjustments.
1. Strength Training is Key
Nothing preserves or builds muscle like resistance training. This stimulates muscle protein synthesis, counteracting age-related decline.
Best Strength Training Tips for Men:
- Train at least 2–3 times per week using free weights, machines, or resistance bands.
- Focus on compound exercises:
- Squats
- Deadlifts
- Bench Press
- Pull-Ups
- Rows
- Use progressive overload — gradually increase weights or resistance to challenge muscles.
- Include balance and stability work to reduce fall risk.
Example Weekly Plan:
- Day 1 – Upper Body Strength (Bench Press, Rows, Shoulder Press, Pull-Ups)
- Day 2 – Lower Body Strength (Squats, Deadlifts, Lunges, Calf Raises)
- Day 3 – Full Body Circuit + Core Work
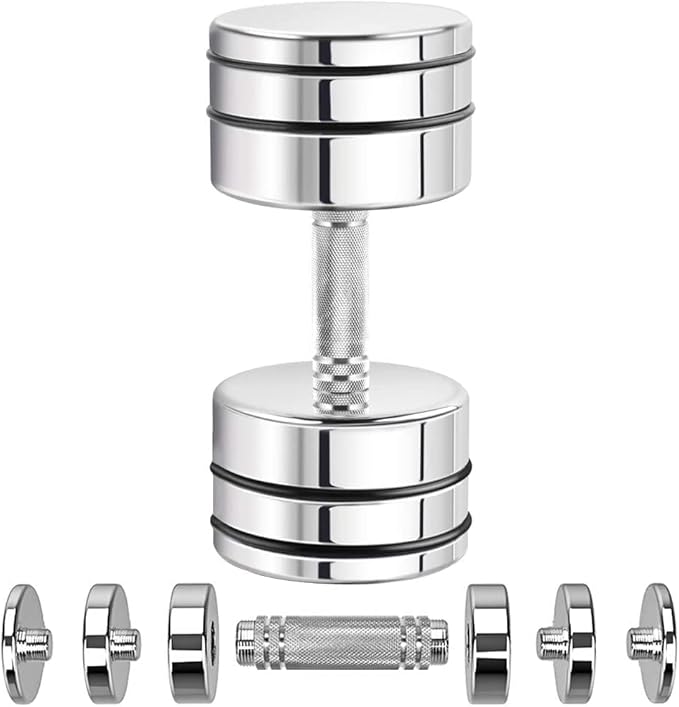
If you want to start strength training at home, a good adjustable dumbbell set like Amazon Brand – Symactive Ultracompact Smart Adjustable Chrome Steel Dumbbells is a great investment.
2. Eat for Muscle Preservation
Muscle growth depends heavily on nutrition — particularly protein intake.
Protein Recommendations
- Men over 40 should aim for 1.2–2.0 grams of protein per kg of body weight daily.
- Spread protein evenly across meals to optimize muscle protein synthesis.
Best Protein Sources

- Lean meats (chicken, turkey, beef)
- Fish (salmon, tuna, cod)
- Eggs and dairy (Greek yogurt, cottage cheese)
- Plant-based proteins (lentils, chickpeas, quinoa, tofu)
Other Nutrients That Help
- Omega-3 fatty acids – Reduce inflammation and aid recovery.
- Vitamin D – Supports muscle function and strength.
- Creatine – Helps increase power output during training.
To easily boost your protein intake, consider adding a high-quality whey protein like BON PURE WHEY to your diet
3. Stay Physically Active All Day
Even outside the gym, movement matters. Long periods of sitting can accelerate muscle breakdown.
Daily Activity Tips:
- Take short walking breaks every hour.
- Do light stretching or bodyweight squats during work breaks.
- Take the stairs instead of the elevator.
- Manage Hormone Levels
Low testosterone is a major contributor to muscle loss in men. If you have symptoms like low energy, reduced libido, and poor recovery, talk to your doctor about:
- Lifestyle fixes – Better sleep, reduced stress, regular strength training.
- Nutrient optimization – Zinc, magnesium, vitamin D.
- Medical options – Testosterone replacement therapy (only under professional guidance).
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential for muscle recovery and joint health. A top choice is Carbamide Forte Omega 3 Fish Oil
5. Prioritize Recovery
Muscles grow during rest, not while training. Ensure:
- 7–9 hours of sleep nightly.
- Rest days between heavy workouts.
- Adequate hydration (2–3 liters/day).
Myths About Muscle Loss and Aging
- “It’s inevitable — nothing can be done.”
✅ False. Studies show older adults can regain muscle mass with proper training and diet. - “Only heavy weights work.”
✅ Not true. Moderate weights with proper form and higher reps can still stimulate growth. - “Protein shakes are mandatory.”
✅ They’re convenient but not essential if you meet protein needs through food.

Sample Meal Plan for Muscle Preservation in Men Over 40
|
Meal |
Foods |
|
Breakfast |
3 eggs, spinach, whole-grain toast, Greek yogurt |
|
Snack |
Protein shake with banana and peanut butter |
|
Lunch |
Grilled chicken breast, quinoa, mixed vegetables |
|
Snack |
Cottage cheese with berries |
|
Dinner |
Salmon, sweet potato, broccoli |
|
Evening |
Handful of almonds or casein protein |
Muscle loss in men is a natural part of aging — but it’s not a life sentence. With strength training, protein-rich nutrition, and an active lifestyle, you can not only slow muscle loss but actually regain strength, mobility, and confidence.
The earlier you start, the better — but even men in their 60s, 70s, and beyond can benefit from these strategies. Your muscle health today shapes your independence tomorrow, so don’t wait to take action.